Table of Contents
- What is Erectile Dysfunction?
- Understanding the Causes of Neurogenic Erectile Dysfunction
- The Role of Testosterone in Erectile Dysfunction
- Medical Conditions and Erectile Dysfunction
- Age and ED: The Vascular Connection and Blood Flow
- Neuroanatomy and Neurophysiology of Erection
- Psychogenic ED: A Treatable Form of Erectile Dysfunction
- Treatment Options for Psychogenic ED
- Lifestyle Changes for Treating Erectile Dysfunction
- Conclusion
What is Erectile Dysfunction?
Understanding the Causes of Neurogenic Erectile Dysfunction
ED is generally classified into different categories based on its causes:
Psychogenic ED: This is related to psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, or depression.
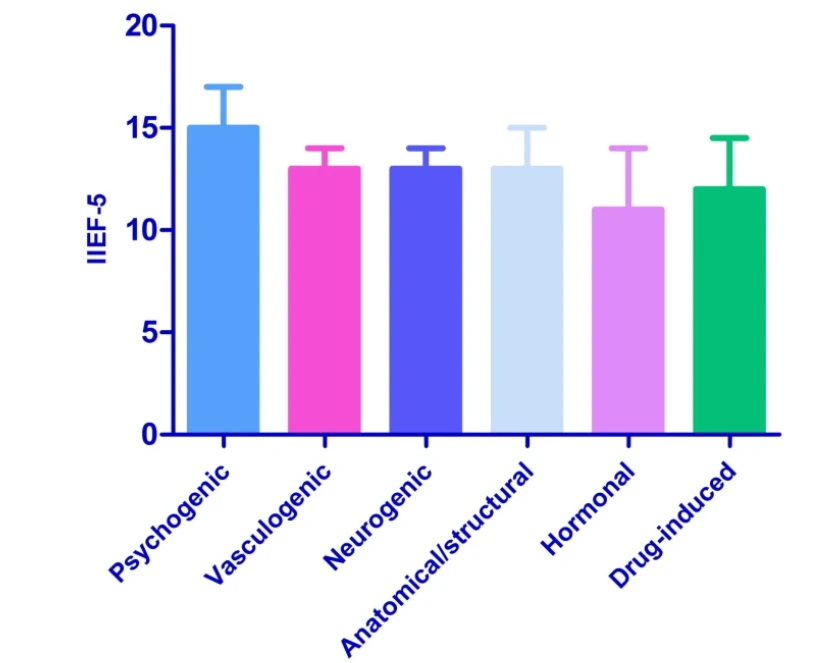
Vasculogenic ED: This type involves issues with blood flow to the penis, often linked to conditions like heart disease or diabetes. The IIEF-5 scores for vasculogenic ED may vary but often indicate a significant issue.
Neurogenic ED: Also known as neurogenic erectile dysfunction, this type is caused by nerve damage, which might be due to conditions like multiple sclerosis or spinal cord injuries. Understanding the neural pathways involved in erection is crucial to effectively assess and address neurogenic ED.
Anatomical/Structural ED: This includes physical abnormalities of the penis, such as Peyronie’s disease.
Hormonal ED: This is related to hormone imbalances, often involving low testosterone levels.
Drug-induced ED: Certain medications can cause ED as a side effect, including some blood pressure medications, antidepressants, and more.
The Role of Testosterone in Erectile Dysfunction
Testosterone plays a crucial role in maintaining erectile function. This hormone is essential for regulating the production of nitric oxide, a molecule that relaxes the smooth muscle in the penis, allowing for increased blood flow and an erection. Additionally, testosterone helps maintain the health of penile tissue and the nerves that control erections. A blood test is essential to confirm testosterone deficiency before considering treatment options.
Studies have shown that men with testosterone deficiency are more likely to experience erectile dysfunction (ED). Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) can improve erectile function in men with hypogonadism, a condition characterized by low testosterone levels. However, it’s important to understand that TRT is not a cure-all for ED. Other underlying medical conditions or lifestyle factors may also need to be addressed to achieve the best results. Testosterone therapy and testosterone treatment can improve symptoms of low testosterone, but they come with potential risks and should be considered carefully. If you suspect low testosterone might be affecting your sexual health, consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment options.
Medical Conditions and Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can often be a symptom of an underlying medical condition. Several common medical conditions can contribute to ED, including:
Heart Disease: High blood pressure, high cholesterol, and atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) can reduce blood flow to the penis, making it difficult to achieve or maintain an erection.
Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves and blood vessels that control erection, leading to ED.
Prostate Cancer: Both prostate cancer and its treatments can damage the nerves and blood vessels that control erection, resulting in ED.
Neurological Disorders: Conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and spinal cord injury can damage the nerves that control erection, leading to ED.
Sleep Apnea: Obstructive sleep apnea can reduce oxygen levels in the blood, which can contribute to ED.
If you are experiencing difficulty getting or maintaining an erection, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider. ED can be a symptom of an underlying medical condition that needs to be addressed. Proper diagnosis and treatment of these conditions can significantly improve erectile function and overall health.
Age and ED: The Vascular Connection and Blood Flow
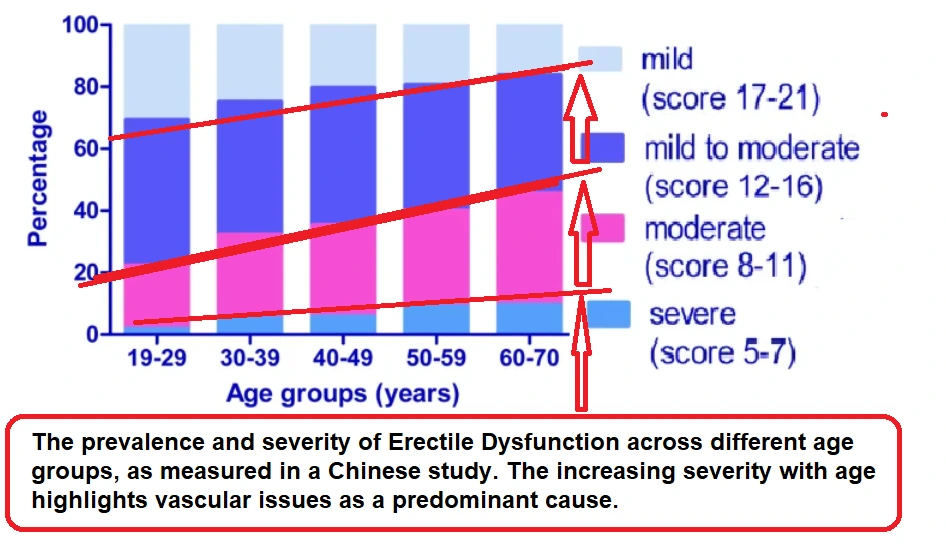
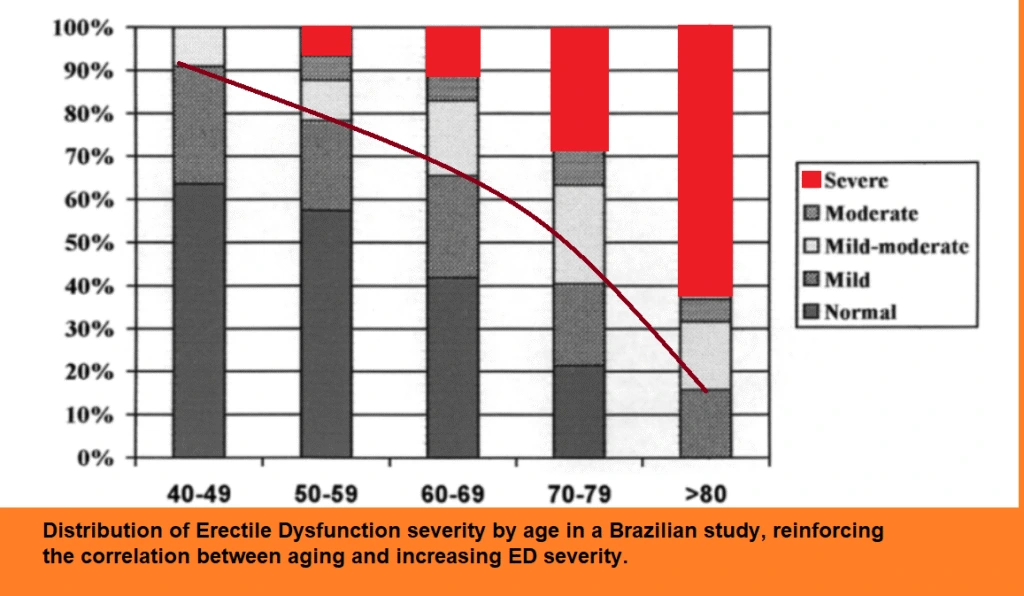
One of the most critical factors in the development of ED is age. Data from both China and Brazil, as illustrated in the charts, indicate a clear relationship between age and the likelihood of ED. The prevalence of ED increases significantly with age, but it’s important to note that this is not necessarily due to psychogenic factors.
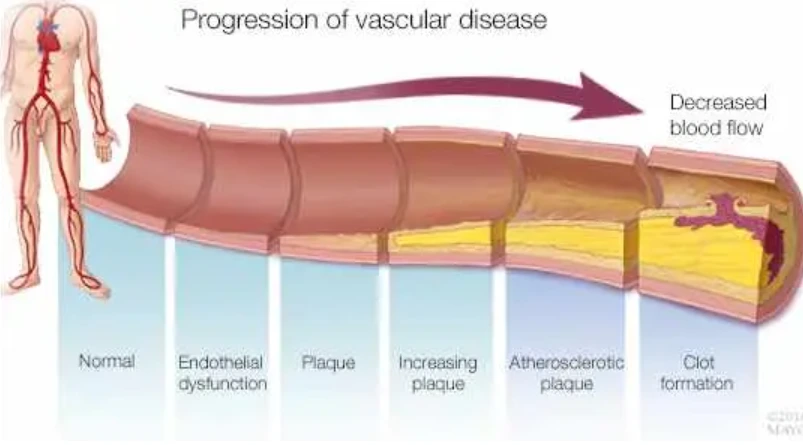
Instead, the increasing severity of ED with age suggests that vascular issues—such as impaired blood flow to the penis—are the predominant cause. This underscores the importance of considering vascular health in the assessment and treatment of ED, particularly in older men.
Neuroanatomy and Neurophysiology of Erection
The process of erection involves a complex interplay between the central nervous system, the spinal cord, and the peripheral nerves. The central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord, plays a crucial role in regulating erection by sending signals to the peripheral nerves that control the smooth muscle in the penis.
The peripheral nerves involved in erection include the dorsal nerve of the penis, which carries sensory information from the penis to the spinal cord, and the cavernous nerves, which carry motor signals from the spinal cord to the smooth muscle in the penis. During an erection, the smooth muscle in the penis, including the corpora cavernosa and the corpus spongiosum, relaxes and fills with blood, allowing for increased blood flow and an erection.
Damage to the nerves that control erection, such as from spinal cord injuries or neurological disorders, can lead to erectile dysfunction (ED). Additionally, conditions that affect blood flow to the penis, such as heart disease or high blood pressure, can also contribute to ED. Understanding the neuroanatomy and neurophysiology of erection can help in diagnosing and treating ED effectively. If you suspect that nerve damage or blood flow issues are affecting your erectile function, seek medical advice for appropriate interventions.
Psychogenic ED: A Treatable Form of Erectile Dysfunction
Psychogenic erectile dysfunction (ED) is a type of ED that stems from psychological factors such as anxiety, depression, and stress. It’s estimated that up to 20% of men with ED have psychogenic ED. This form of ED can be effectively treated with a combination of therapy, lifestyle changes, and medication.
Psychogenic ED can be triggered by various psychological factors, including:
Anxiety and Stress: High levels of anxiety and stress can interfere with the ability to achieve and maintain an erection.
Depression: Depression can lead to a decrease in libido and erectile function.
Relationship Issues: Problems within a relationship can contribute to psychogenic ED.
Trauma: Traumatic experiences, such as sexual abuse, can also lead to psychogenic ED.
Symptoms of psychogenic ED may include:
Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection
Decreased libido
Premature ejaculation
Difficulty with orgasm
Understanding that psychogenic ED is a treatable condition is crucial. Addressing the underlying psychological issues can significantly improve erectile function and overall well-being.
Treatment Options for Psychogenic ED
Treating psychogenic ED typically involves a multifaceted approach that includes therapy, lifestyle changes, and medication. Therapy can help address the psychological issues contributing to ED, such as anxiety and depression. Lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise and a healthy diet, can also enhance erectile function.
Medications that may be used to treat psychogenic ED include:
- Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors (PDE5 Inhibitors): Medications like sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), and vardenafil (Levitra) can improve erectile function by increasing blood flow to the penis.
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs): Medications such as fluoxetine (Prozac) can help treat depression and anxiety, which can contribute to psychogenic ED.
Combining these treatments can provide a comprehensive approach to managing psychogenic ED, helping men regain their confidence and improve their sexual health.
The Role of the IIEF-5
The IIEF-5 is a widely used tool for diagnosing the severity of ED. It includes questions that assess various aspects of erectile function, helping healthcare providers determine the best course of treatment. However, the IIEF-5 is not perfect, and its ability to differentiate between different types of ED may have limitations.
Taking the First Step with Testosterone Replacement Therapy
If you’re experiencing symptoms of ED, it’s crucial to recognize that this is not something to be ashamed of. ED is a treatable condition, and many effective treatments are available. From medications like Viagra to lifestyle changes, psychological support, and even surgical options, there is a solution that can work for you.
Lifestyle Changes for Treating Erectile Dysfunction
Lifestyle changes can play a significant role in treating erectile dysfunction (ED). Making healthy lifestyle choices can improve erectile function and overall health. Here are some lifestyle changes that may help treat ED:
Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can enhance erectile function by increasing blood flow to the penis and reducing stress.
Healthy Diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support better erectile function.
Weight Loss: Shedding excess weight can improve erectile function by reducing inflammation and enhancing blood flow.
Stress Reduction: Finding ways to manage stress, such as through meditation or yoga, can positively impact erectile function.
Quitting Smoking: Smoking can damage blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the penis, so quitting smoking can improve erectile function.
Limiting Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can contribute to ED, so moderating alcohol consumption can help improve erectile function.
It’s essential to note that lifestyle changes should be made in conjunction with medical treatment if necessary. Always consult with a healthcare provider before making significant changes to your lifestyle to ensure the best approach for treating erectile dysfunction.
Conclusion
Erectile Dysfunction is more common than you might think, affecting men of all ages. Whether the cause is psychological, physical, or a combination of factors, treatments are available. The first step is acknowledging the issue and seeking help from a healthcare provider. With the right approach, ED can be managed effectively, allowing you to enjoy a healthy, satisfying sex life.
Peak Masculinity
Starts Here

By Dr. Ryan Welter
August 15, 2025




